| |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
BDD Electrode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Water treatment with BDD (Boron
Doped Diamond) electrodes can be
divided into the areas of
disinfecting and waste water
treatment. Both areas have, in
common, the fact that with the
assistance of an electrochemical
procedure impurities such as
bacteria, viruses, algae, oils,
emulsions, chemical and
pharmaceutical residues may be
removed. A remarkable fact about
using BDD electrodes is the
extremely high over-voltage
exhibited for water electrolysis.
Instead of the production of oxygen
extremely effective OH radicals are
formed directly from the water
without any additional chemical
input. Through the efficient use of
electrochemical |
|
procedures, using
BDD electrodes, it
is possible to
replace existing
procedures and to be
prepared for further
future requirements.
It is possible to
save both on space
and maintenance
costs and to be
ready for the future
through a simple
scale up procedure.
BDD properties
■
Electrically
conductive
(Typically
0.4~1.0 x 10-3
Ω.cm)
■
Wide
electrochemical
window for
e.g. O3
and OH
production
■
Bio-compatible
■
Varied
surface
terminations
possible
■
Chemically
inert up to
600 oC
■
No-fouling
■
Mechanically
robust
■
No-Porous
Electrochemical
window
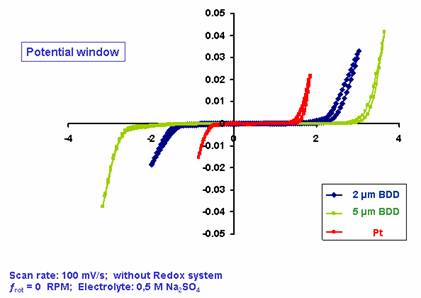
Courtesy of Karl-Winnacker-institut
|
|
Electrochemical
applications:
■
Decomposition of
cyanide in hardening
shop wastewater.
■ CN reduction
(61h): 69.4% (PbO2),
95.3%(BDD)
■ COD
reduction (61h):
57.6%, 80.4% (BDD)
|
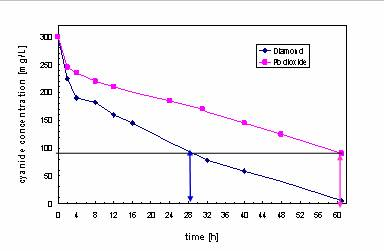
Courtesy of Dr.
Horstkotte, TU
Munich |
|
|
|
|
|